Accessing the Internet and Web
We will need:
- A computer with an operating system, such as MAC OS, Windows, or UNIX, that supports Internet protocols
- Communications equipment such as a modem, ISDN adapter, or Ethernet card
- An Internet service provider (ISP)
- Web browser software such as Safari, Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome or Internet Explorer
The Hypertext Concept:
Hypertext is a way of presenting information so that the order in which it’s read is left up to the reader.
Hyperlinks are underlined or highlighted words that can be used to view another document or Web page.
Hypermedia refers to a link to multimedia, such as music and movies.
The Web is a distributed hypermedia system or a system where the responsibility for creating content is distributed among many people.
Web Browsers and Servers:
Web browsers display a Web document and enable users to link to other Web pages. The first browsers were text-only. Mosaic was the first graphical browser. Web servers respond to the requests of browsers. They find and send requested resources back to the browser.
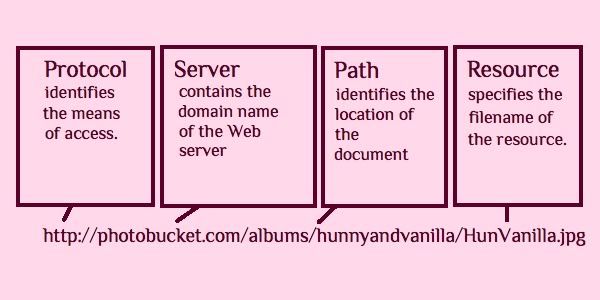
Web Addresses (URLs) are an addressing system that identifies where a Web resource is located. The uniform resource locator (URL) is the standard used to identify Web resources. The URL consists of:
Examples of Top-Level Domains
Uploading and Downloading:
- .com – commercial businesses
- .edu – educational institutions
- .gov – government agencies
- .mil – military organisations
- .net – network providers
- .org – nonprofit organisations
More than half of my music and video collections I downloaded from the Internet but I know I'm not the only one and posting things like this is how I contribute back to the computing community.
Downloading is when document or file is transferred from another computer to our computer.
Uploading is when files transferred from our computer to another computer.
Finding Information on the Web:
There are ways to find information on the Web:
- Browse or surf the Web – This involves linking from one Web page to another, and so forth.
- Search the Web – This method involves using search engines to locate Web pages with the information we’re looking for.
- Subject guides – Web pages are grouped under headings.
To use a search engine, we:
- Choose a search engine (Google, Yahoo, MSN, Lycos, Alta-Vistaetc.).
- Type in one or more words describing your topic.
Using Search Techniques
Learning a few search techniques can increase the accuracy of Web searches. Searches using search operators will improve search performance.
Most search engines use the following search operators:
- Inclusion/exclusion operators
- Wild cards
- Phrases
- Boolean operators
Not using search operators:
| Words Entered | Possible Results: Web pages containing |
| Fire station | Fire station Fire station |
Using search operators:
| Words Entered | Possible Results: Web pages containing |
| +Fire+station | Fire station |
| +Fire+station* | Fire station Fire stations |
| +Fire-station* | Fire |
| “Fire station” | Fire station |
| Fire and station | Fire station |
| Fire or station | Fire station Fire station |
| Fire not station | Fire |
E-Mail: Staying in Touch:
E-mail is short for electronic mail. It’s the most popular of the Internet services. Messages are sent and received in a few seconds. Attachments such as photos, music files, and any document may be sent with the message.
E-Mail Addresses
myname@someserver.com
User’s name@name of the server that the user is on
myname@someserver.com
User’s name@name of the server that the user is on
e.g.: danielle.ivory22@gmail.com
Instant Messaging: E-Mailing Made Faster
Instant Messaging: E-Mailing Made Faster
Instant messaging systems let a user know when a friend or business associate is online. It provides a means of communicating through real-time, text-based conversations.
IRC: Text Chatting in Real Time:
Internet relay chat consists of real-time, text-based conversations. Chat groups are divided into channels that cover a specific topic.
Usenet:
Usenet is the part of the Internet which enables users to participate in discussions and newsgroups. Usenet newsgroups are organised into hierarchies (categories) and subcategories. Subcategories include Standard, Alt, Biz, and Local newsgroups.
Standard Newsgroup Subcategories:
| comp | computer applications, databases, multimedia |
| misc | activism, books, business, health |
| sci | chemistry, archeology, math |
| soc | human rights, world cultures |
| talk | Euthanasia, gun control, religion |
| news | Usenet announcements |
| rec | sports, gardening, bicycles |
Listservs: Electronic Mail Lists:
A listserv is an automatic list server. Mail is sent to everyone on the list when e-mail is generated. It is similar to a newsgroup or a forum.
Alright, that's all for the introduction to Internet! Next post would be on discussion on how to relate what we have learned so far to our daily lives and of course as a Muslim.






Be First to Post Comment !
Post a Comment